eBook
Learn how to get your micromirror development on the right track.
Managing the six key design decisions in creating MEMS mirrors.
What you will learn in this ebook?

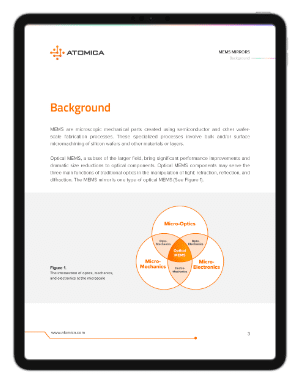
MEMS mirrors have evolved over the last 20+ years with an ever evolving set of applications. Take a quick look at the history and markets changed by these tiny mirrors.

Take a deep dive into the six critical architectural trade-offs that will determine the final design and production process for a MEMS mirror.

It is relatively easy for R&D teams to develop a MEMS mirror that works in a single-unit prototype. Learn how to choose the right development and manufacturing partner.
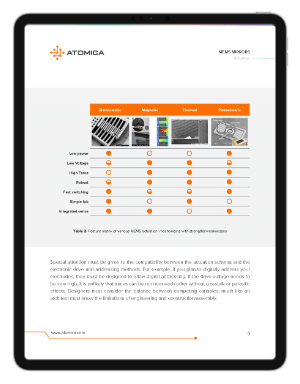
Numerous design specifications must be considered in the development of any MEMS mirror product. These are broken down into six key engineering disciplines:
01
Mechanical Specifications
For most applications, the size of the mirror is the primary mechanical issue. MEMS mirrors are typically in the range of five microns to five millimeters, leading to vastly different methods of manufacture, materials, and actuation.
02
Optical Specifications
In most applications, the mirror’s reflectivity is important and will vary based on the metal and coating processes used in fabrication.
03
Actuation
Depending on the forces, speed, and power requirements, the actuation and drive circuitry (coupled with the mechanical design) determine the mechanical behavior of the mirror.
04
Control
Many questions from a controls point of view: Can the electrodes be driven by high or low voltage? Analog or digital addressing? Steering or snap-in? Resonant or non-resonant mode? Open-loop or closed-loop feedback and mirror position control?
05
Packaging
The device needs to be mounted for wiring and packaged to enable a commercial product that meets the application requirements.
06
Integration
Once the MEMS mirror module is complete, the final challenge involves the placement and integration of that module into the broader system.